Post Vaginal Delivery with Impending Silent Abdominal Catastrophe: A Case of Vernix Caseosa Peritonitis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31436/imjm.v22i4.2092Keywords:
vernix caseosa, peritonitis, radiological imaging, diagnostic laparoscopic, steroids, IVIG, anti-inflammatoryAbstract
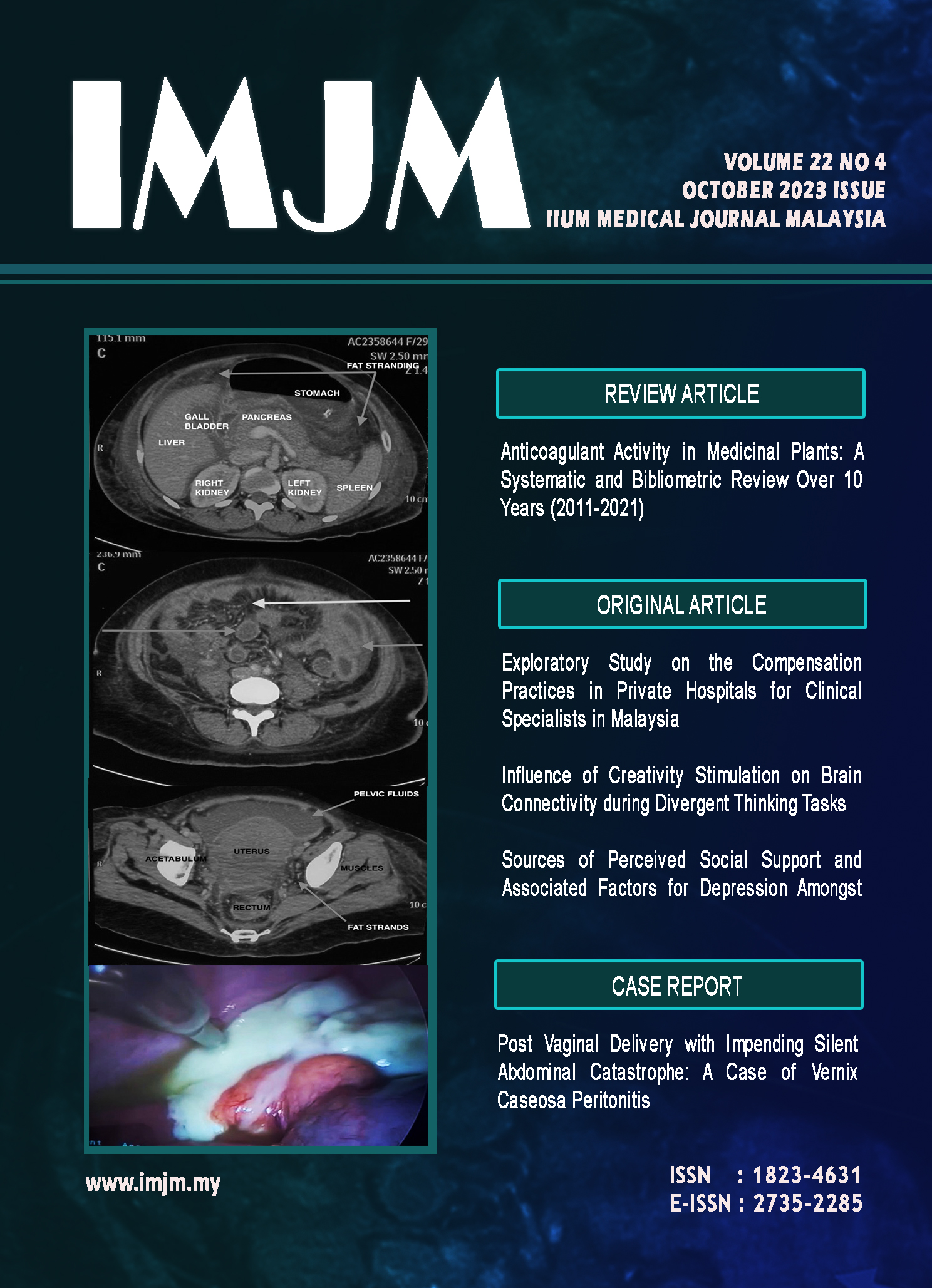
Vernix caseosa peritonitis (VCP) is a rare condition previously thought to be a complication of Caesarean section caused by the spillage of amniotic fluid and or meconium into the maternal peritoneal cavity during operation.1 This triggered an inflammatory reaction symptom such as an acute abdomen. A total of 34 cases has been reported since 1976.2 Nine of the 10 cases reported have been diagnosed in postpartum period after uneventful Caesarean section and only three reported cases of antenatal leakage since in 1998.3 VCP following vaginal delivery was first reported in 2013, involving a 28 year old with one previous scar who developed acute abdomen symptoms as early as 3 hours post vacuum delivery, with initial diagnosis of possible uterine scar rupture.4 Here we report a case of VCP in a post spontaneous vaginal delivery who presented with impending catastrophe and survived the ordeal.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
All material submitted for publication is assumed to be submitted exclusively to the IIUM Medical Journal Malaysia (IMJM) unless the contrary is stated. Manuscript decisions are based on a double-blinded peer review process. The Editor retains the right to determine the style and if necessary, edit and shorten any material accepted for publication.
IMJM retain copyright to all the articles published in the journal. All final ‘proof’ submissions must be accompanied by a completed Copyright Assignment Form, duly signed by all authors. The author(s) or copyright owner(s) irrevocably grant(s) to any third party, in advance and in perpetuity, the right to use, reproduce or disseminate the research article in its entirety or in part, in any format or medium, provided that no substantive errors are introduced in the process, proper attribution of authorship and correct citation details are given, and that the bibliographic details are not changed. If the article is reproduced or disseminated in part, this must be clearly and unequivocally indicated.